Products Description
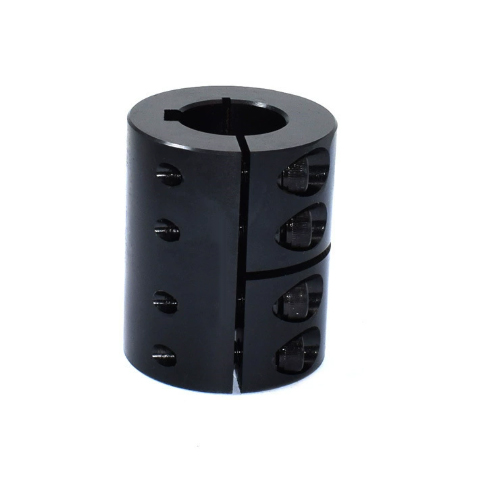
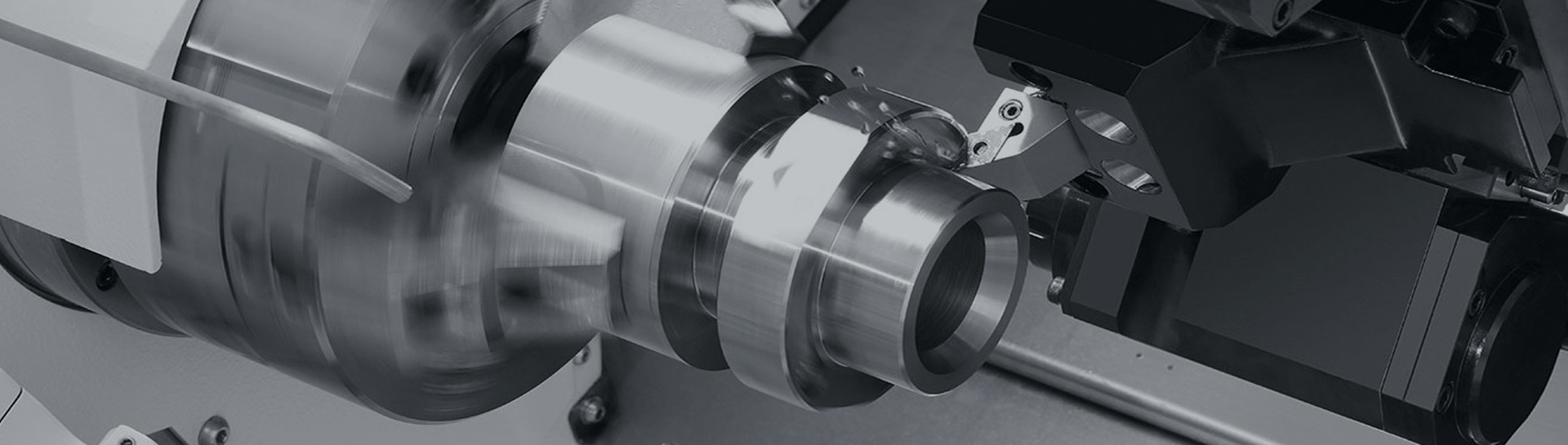
Clamp Shell CouplingIt Is A Rigid Coupling With A Simple Structure, Consisting Of Two Axially Divided Clamping Shells (usually Made Of Cast Iron Or Cast Steel) And Connecting Bolts. It Is Named After The Fact That The Two Half Clamping Shells Achieve Transmission By Clamping The Shaft Section With Bolts. The Core Design Is To Use The Tight Fit Between The Inner Wall Of The Clamping Shell And The Shaft To Generate Frictional Force And Transmit Torque. Some Models Will Process Key Slots On The Inner Side Of The Clamping Shell, Which Will Be Combined With Flat Keys To Further Enhance The Torque Transmission Capability.
During Installation, Wrap The Two Halves Of The Clamping Shell Around The Two Shaft Ends That Need To Be Connected, Tighten The Clamping Shell Radially With High-strength Bolts, And Use Clamping Force To Fix The Shaft Section And Achieve Power Transmission. This Type Of Coupling Can Be Assembled And Disassembled Without The Need For Axial Movement Of The Shaft System, Making Installation And Maintenance Extremely Convenient, Especially Suitable For Working Conditions Where The Shaft End Cannot Be Disassembled Axially. However, Due To The Lack Of Elastic Components, It Is Impossible To Compensate For Axial Offset (radial And Angular Deviations Need To Be Controlled Within 0.1mm/m), And It Does Not Have Shock Absorption Function, Requiring High Accuracy For The Alignment Of The Two Axes.
The Clamping Coupling Has A Wide Range Of Torque Transmission (usually 50~5000N · M), And The Allowable Speed Decreases With The Increase Of Diameter (about 3000r/min For Diameter 50mm And 600r/min For Diameter 300mm). It Is Suitable For Low-speed And Stable Load Transmission Systems, Such As Shaft Connections Of Water Pumps, Fans, Conveyor Belts And Other Equipment. Its Advantages Lie In Low Cost, Compact Structure, And Weight That Is Only 60% To 70% Of The Same Specification Flange Coupling; The Disadvantage Is That Long-term Use May Result In A Decrease In Clamping Force Due To Loose Bolts, Requiring Regular Checks Of Tightening Torque, And Vibration Noise May Be Generated Due To Centrifugal Force During High-speed Operation.
When Selecting, The Size Of The Clamping Shell Should Be Matched According To The Shaft Diameter, Maximum Torque, And Speed. In Terms Of Material, Cast Iron Is Suitable For Light Load And Room Temperature Conditions, While Cast Steel Can Withstand Medium To Heavy Loads And Short-term Impacts. Stainless Steel Material Can Also Be Used For Corrosion Protection In Special Environments.